Table of Contents
Vig. Vigorish. Juice. You might hear these gambling terms uttered by sports bettors and wonder what they mean.
They’re all the same thing. The vig (short for vigorish) in sports betting is the house edge.
Though “house edge” is a more common term in the casino world, it gives us important context here. In sports betting, the vig is how a sportsbook makes money.
Sports betting sites need to turn a profit, so they work a slight advantage into each bet.
Below, we’ll show you how the vig works, how to calculate it and why it’s important.
Vig & Odds Explained
Sportsbooks couch the vig in the odds they offer. You won’t find any “vig” section within a sportsbook app, as the betting odds listed for a match or game already include the vig.
Let’s say an evenly matched game is coming up where oddsmakers give each team a 50-50 shot to win. The odds on the game would be +100. In other words, a winning $100 bet would pay a $100 profit.
If you’ve spent time on a sports betting mobile app, you know this isn’t how most odds look. In an even matchup, sports betting sites will typically offer odds of around -110 on either side.
A $100 bet on those odds would pay out a $90.91 profit, leaving about 9% of your total bet with the sportsbook.
That 9% or $9.09 represents the sportsbook’s share and is essentially a surcharge for taking and processing your bet.
The Vig Plays Both Sides
There’s no guarantee bettors will flock to one side of a bet and potentially give the sportsbook an easy profit. Instead, operators seek to take similar numbers of wagers on both sides of any given betting market.
With vig built into those odds, sportsbooks can often guarantee a profit, regardless of the game or market’s outcome.
They often do this by setting their plus odds lower than their minus odds. This forces bettors to risk more money on favorites and protects operators from losing too much money on upsets.
For example, a heavy moneyline favorite in an NBA game might have -700 odds, while the underdog would have odds around +500. You’ll never see the reverse of -500 on a favorite and +700 on the underdog, as the sportsbook would likely lose money in the event of an upset.
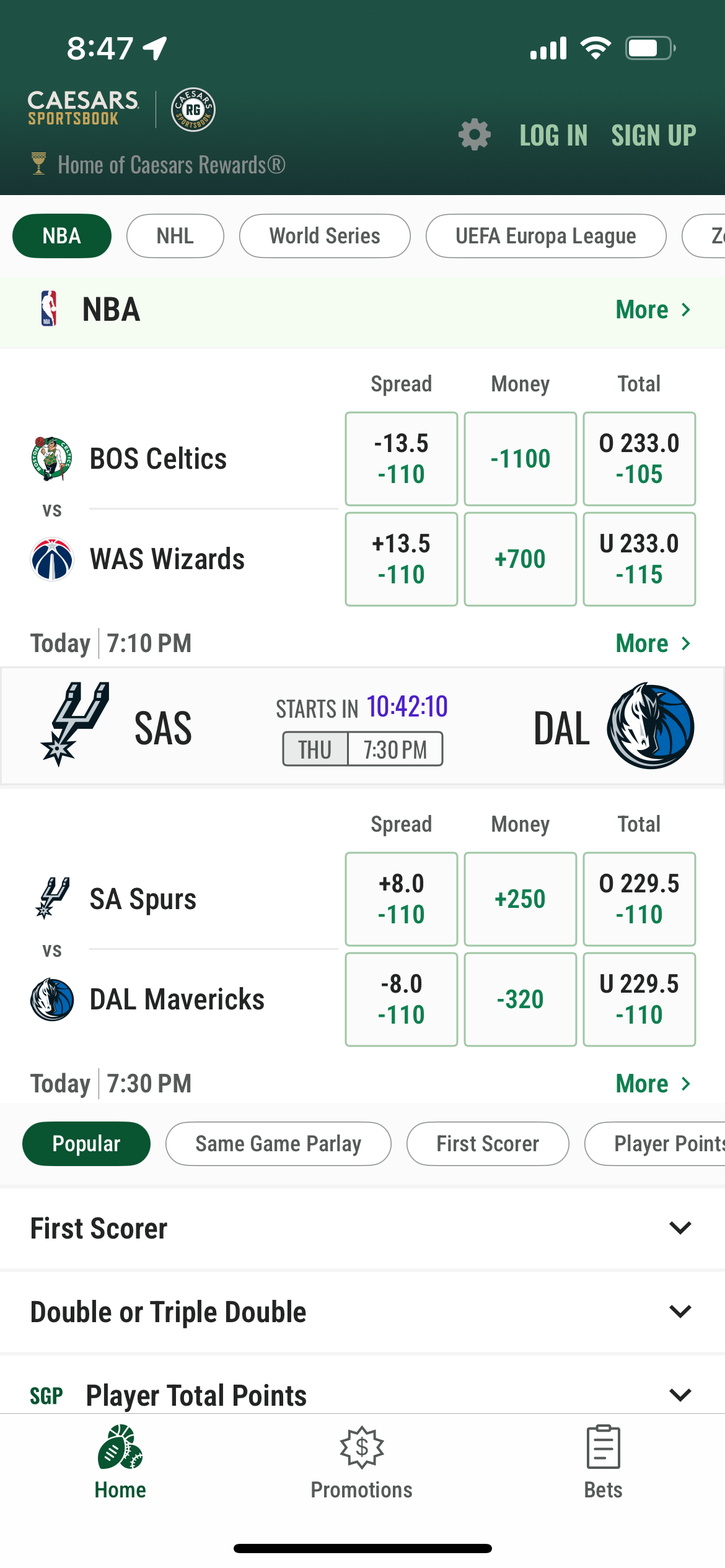
A clear example of how the vig works occurred during the men’s 2024 NCAA Tournament. The first two rounds of March Madness saw an unusual dearth of upsets with moneyline favorites going 36-12 in the first two rounds of the tournament, including 15-1 in the Round of 32.
Normally, that would be bad news for sportsbooks, as they tend to make money on underdogs winning because fewer people bet on them.
In many cases, however, the moneyline favorites had such extreme odds (several were around -1000) that it was difficult to win much money on them. Accordingly, sportsbooks still came out on top even though the favored team won 75% of the time.
https://x.com/capjack2000/status/1772285665050280076?s=46
This is a perfect example of how the vig protects sportsbooks from losing money even when the public gets the majority of their bets right.
How To Calculate The Vig
You can calculate the vig on a set of bets yourself using this formula:
(Favorite odds/(Favorite odds + 100) x 100) + (100/(Underdog odds + 100) x 100) – 100 = Vig
Note: You do not need to include the “-” or use negative numbers in the favorite odds sections of the formula. Use the absolute value. If the odds are -200, use 200.
Let’s use these hypothetical NFL odds to calculate the vig.
- Chicago Bears: +155
- Seattle Seahawks: -180
Plugging these into the formula gets us:
(180/(180 + 100) x 100) + (100/(155 + 100) x 100) – 100 = 3.51%
Doing each side of the formula (consider the “+” the center point) gets you a positive number and a negative number. In this case, 64.29 and -60.78. Adding the two gets us our vig of 3.51.
Does The Vig Matter?
Yes, the vig is consequential. The vig is essential to your sports betting experience, whether or not you take the time to calculate it yourself.
If you’re a casual bettor, chances are you simply like to place your wager and hope for the best. That’s completely fine, especially if you prefer to stick to one sportsbook rather than researching all the odds at various books.
On the other hand, diehard sports fans or seasoned bettors seeking potential profit should pay close attention to the vig. The vig can and often does vary by sportsbook.
If you find competing books with differing vig on a particular bet, you’ll want to place your wager at the one with the lower juice.
Over time, tiny differences in vig and payout can add up (especially on bigger bets), helping you hone your betting strategy and hopefully bring home some profitable wins. We recommend betting in units if you’re seeking a profit in the long run.
Does One Sportsbook Have the Lowest Vig?
If one sportsbook consistently offered the lowest vig, it might run its competition out of business. For the most part, sportsbooks compete with one another in terms of odds and corresponding vigorish.
This results in a bettor’s market, provided you have multiple online sportsbooks available in your state.
If possible, shop around. You don’t need to figure out the vig for each sportsbook, either, as it’s already built into the odds. If Caesars Sportsbook offers odds of +155 on your desired bet but DraftKings Sportsbook has the same bet at +162, DraftKings is the better choice.
The odds tell the whole story without the need to calculate the vig.
How To Beat The Vig
If you’re trying to beat the vig, we’ve got good news and bad news.
The bad news is that opportunities to beat the vig are few and far between. Sportsbooks must make money, and the vig is how they do it.
The good news is that if you find an odds boost promotion, that can help you avoid the vig if your bet ends up winning. Use promotions and bonuses to your advantage to avoid juice when you can.
Other promos might offer no-juice odds on specific games or matches to eliminate vig in select cases. These promotions are relatively rare, so it’s wise to pounce on them when a sensible option pops up.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a typical vig for a pick'em bet?
A typical vig at a regulated online sportsbook in the U.S. for a 50-50 wager is “-110” or 4.54%. This is common for both spread and over/under bets.
Do offshore online sportsbooks have less vig?
Illegal online sportsbooks often charge less vig. These sportsbooks don’t pay taxes or licensing fees in the U.S. and thus have less overhead costs. They also don’t market their products in the U.S. through channels such as TV and radio, which can be costly for companies.
While paying less vig with offshore operators may be enticing for consumers, we recommend avoiding them. Your money and personal information are less secure.
Is the vig like the rake in poker?
Yes, the “rake” is the percentage of a cash game pot or tournament buy-in that the house takes for hosting the game. This is very similar to the sports betting vig.
What does ovverround mean?
You can translate sports betting odds into an implied probability of an outcome occurring. However, because the odds have a vig, the implied probabilities added together equal more than 100%.
The amount of “overround” expressed as a percentage is not the same as the vig. However, the vig and the overround are functions of each other. It’s important to note that the sports betting odds aren’t a real-life probability for an outcome. Gambling odds are best thought of as a price.



